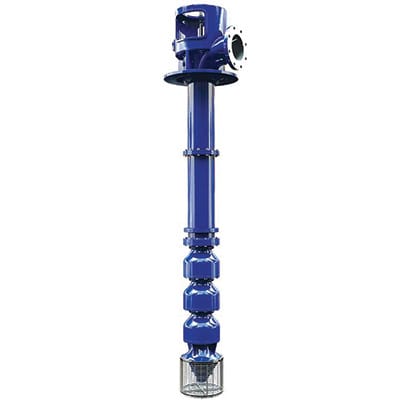
A Vertical Turbine Pump (VTP) is a specialized centrifugal pump designed to move water or other fluids from deep underground sources such as wells, reservoirs, or tanks. These pumps are characterized by their vertical orientation, multi-stage configuration, and ability to handle high flow rates and high heads.
A Vertical Turbine Pump is a vertical shaft pump typically used for pumping water from deep wells or below-ground tanks, especially where the water level is lower than the pump itself. It is often composed of multiple stages to generate sufficient pressure.

| Parameter | Range |
|---|---|
| Flow Rate | Up to 100,000 GPM (22,700 m³/h) |
| Head | Up to 1,500 ft (457 m) |
| Bowl Sizes | 6″ to 40″+ |
| Motor Power | 5 HP to 2000+ HP |
| Materials | Cast iron, bronze, stainless steel, duplex steel |
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Pump Bowl Assembly | Located at the bottom, contains impellers and diffusers that lift and pressurize the fluid. |
| Column Pipe | Long vertical pipe connecting the bowl to the discharge head; houses the line shaft. |
| Line Shaft | Transmits power from the motor at the top to the impellers below. |
| Discharge Head | Located at the surface; supports the motor and directs the fluid to the discharge piping. |
| Motor | Typically electric (above-ground) or diesel engine; powers the pump. |
Working Principle:
-
Fluid enters the pump bowl through a suction bell.
-
One or more impellers lift the fluid and add pressure.
-
The fluid moves upward through the column pipe, powered by the line shaft.
-
At the surface, the discharge head redirects the fluid into the discharge piping.
Key Features:
-
Multistage design: Multiple impellers allow operation at high heads (deep well applications).
-
Vertical configuration: Ideal for deep installations where horizontal pumps can’t be used.
-
Customizable lengths: Column pipes and shafts can be added to match well depth.
-
Bearings (sleeve or bush type) support the long shaft for stability.
Advantages:
-
Suitable for deep well pumping (even >200 meters).
-
High efficiency at large capacities and high pressures.
-
Reliable in continuous-duty applications.
-
Can pump clear, raw, or sea water, and some chemicals (with appropriate materials).
Common Applications:
-
Municipal water supply (deep well extraction)
-
Irrigation systems
-
Industrial water circulation
-
Fire protection systems
-
Power plants (cooling water intake)
-
Desalination plants
Limitations:
-
More complex and costly than submersible or horizontal pumps.
-
Requires regular maintenance, especially shaft bearings and alignment.
-
Needs precise installation and balancing.

 Industrial Water Plant
Industrial Water Plant